Yield to maturity equation 185258-Approximate yield to maturity equation
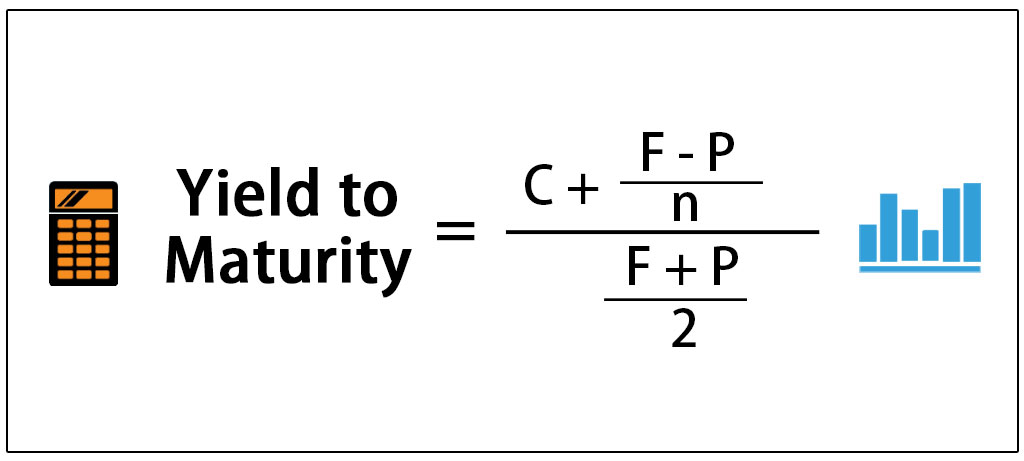
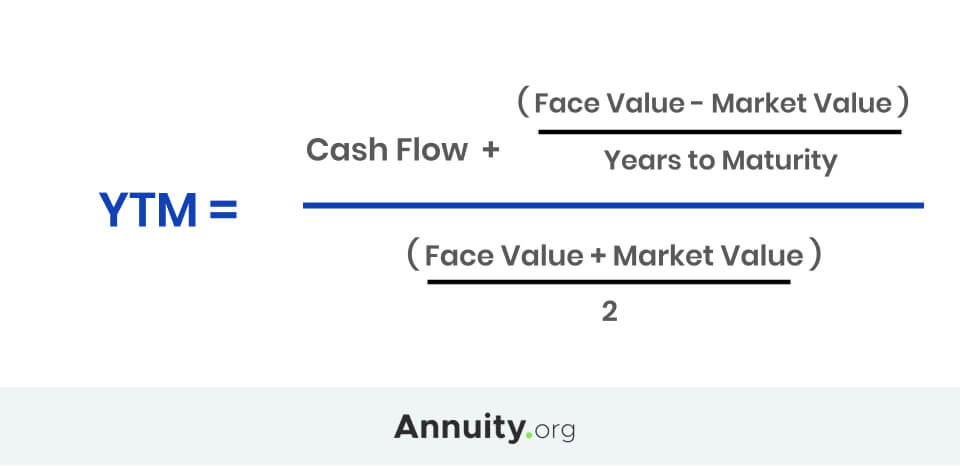
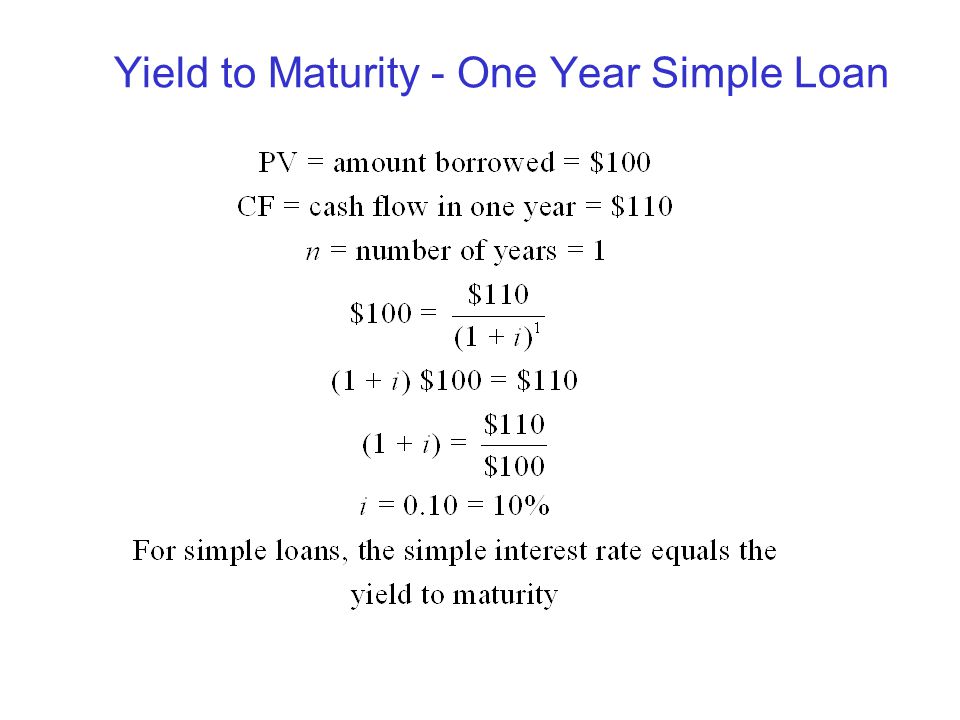
To apply the yield to maturity formula, we need to define the face value, bond price and years to maturity For example, if you purchased a $1,000 for $900 The interest is 8 percent, and it will mature in 12 years, we will plugin the variables C = 1000*008 = 80If your state levies an income tax, the same equation can be used to calculate the Treasuryequivalent yield of a municipal bond issued in your state or the fully taxableequivalent yield of aYield to Maturity Examples C = future cash flows/coupon payments r = discount rate (the yield to maturity) F = Face value of the bond n = number of coupon payments

Vba To Calculate Yield To Maturity Of A Bond
Approximate yield to maturity equation
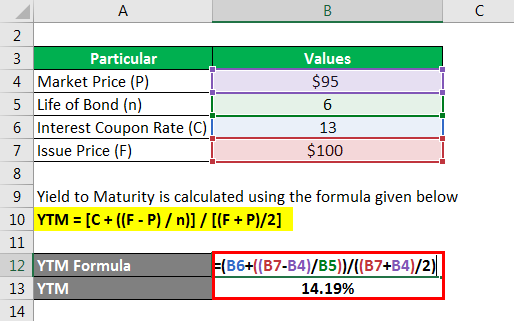
Approximate yield to maturity equation-Yield to maturity formula Where, bond price = the current price of the bond Coupon = Multiple interests received during the investment horizon These are reinvested back at a constant rate Face value = The price of the bond set by the issuerThe bond yield equation is a simple calculation technique when compared to the yield to maturity It is straightforward and clear Moreover, it ignores the time value of money and matured value Recommended Articles This has been a guide to Bond Yield Formula


Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula Method Example Approximation Excel
Formula Under the yield to maturity approach, cost of debt is calculated by solving the following equation for r There is no algebraic solution to the above equation, but we can employ the hitandtrial method We can also use Excel YIELD function Please see the article on YIELD TO MATURITY to study alternative methods for solving for rYield to Maturity (YTM) is the most commonly used and comprehensive measure of risk In fact, if someone talks about just 'Yield' they are most likely referring to Yield to Maturity In simple terms, YTM is the discount rate that makes the present value of the future bond payments (coupons and par) equal to the market price of the bond plusN = number of semiannual periods left to maturity;
The yield to maturity equation is used to determine the total annual return that an investor will receive if an asset such as a bond is held until maturity The basics of the yield to maturity equation requires identifying the original purchase price of the asset, the rate of interest that applies, and the number of years that remain until theUse the Yield Function to Calculate the Answer Type the formula "=Yield(B1,B2,,B4,B5,B6,)" into cell B8 and hit the "Enter" key The result should be percentwhich is the annual yield to maturity of this bondYield can also be represented in the form of current yield Let's again look at our yield to maturity example to understand what is the current yield Current yield, by definition, is the annual rate of return that you receive for the price paid for that bond The formula of current yield Coupon rate / Purchase price
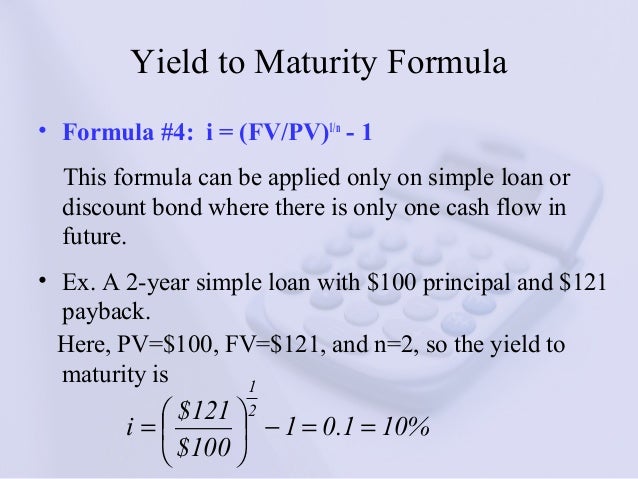
Simple yield to maturity (SYTM) is the approximate annual interest rate at which a bond yields the same return, provided the investor holds the bond until maturity and receives all of the coupon payments You cannot compute the interest rate by hand using the exact equation for yield to maturity (YTM), as that equation is too complexYield to maturity (YTM) is the annual effective return that would be earned on a bond if it is held till its maturity Expressed as an annual percentage, the yield tells investors how much income they will earn each year relative to the cost of their investment Formula to calculate yield to maturityThe formula for calculating the yield to maturity on a zerocoupon bond is Yield To Maturity=(Face Value/Current Bond Price)^(1/Years To Maturity)−1 Consider a $1,000 zerocoupon bond that has



Berk Chapter 8 Valuing Bonds


Microsoft Excel Bond Yield Calculations Tvmcalcs Com
Yield to Maturity 3 Yield of a Bond on a Coupon Date For an ordinary semiannual coupon bond on a coupon date, the yield formula is where c is the coupon rate and T is the maturity of the bond in years Annuity Formula Math result Finance application This formula gives the present value of an annuity of $1The Yield to Maturity Unlike the current yield, the yield to maturity (YTM) measures both current income and expected capital gains or losses The YTM is the internal rate of return of the bond, so it measures the expected compound average annual rate of return if the bond is purchased at the current market price and is held to maturityYield to Maturity (YTM) is the most commonly used and comprehensive measure of risk In fact, if someone talks about just 'Yield' they are most likely referring to Yield to Maturity In simple terms, YTM is the discount rate that makes the present value of the future bond payments (coupons and par) equal to the market price of the bond plus



Yield To Maturity Ytm Formula Interest And Deposit Calculators
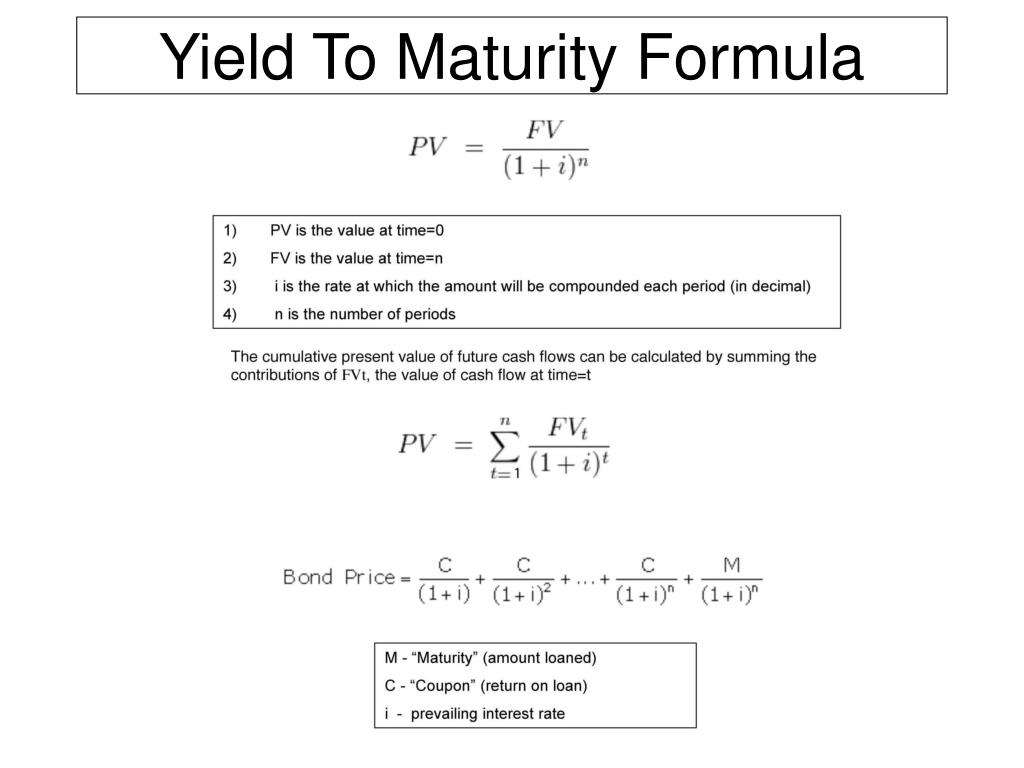


Ppt Yield To Maturity Formula Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
The yield to maturity formula is very simple if the par value equals the market value At that point, the yield to maturity is simply the coupon rate However, this is rarely the case Therefore, for the many times the market value doesn't equal the par value, thePlugging in the calculation formula, you calculate the yield as follows 1 (07/2) 2 – 1 = 7123% To see how the number of annual coupon payments received affects the effective yield on your bond, let us do another effective yield calculation that assumes you receive monthly coupon payments – 12 interest payments each yearHowever, YTM is not current yield – yield to maturity is the discount rate which would set all bond cash flows to the current price of the bond You can find more information (including an estimated formula to calculate YTM) on the yield to maturity calculator page
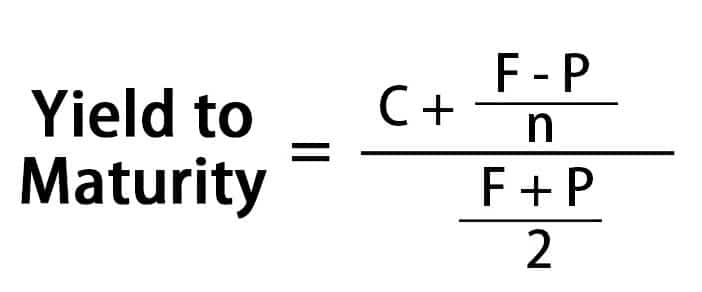


What Is The Approximated Yield To Maturity Ytm Forex Education
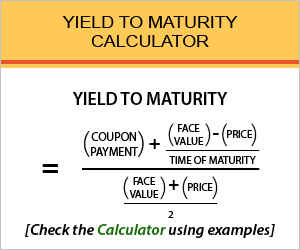


Yield To Maturity Calculator Find Formula Check Example More
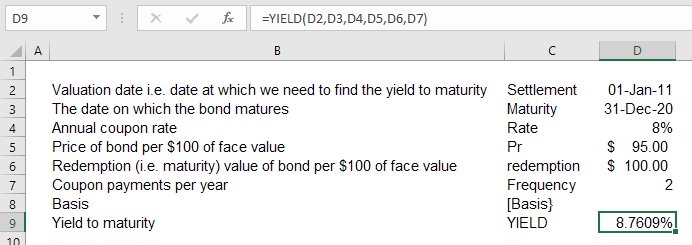
The yield to maturity (YTM), book yield or redemption yield of a bond or other fixedinterest security, such as gilts, is the (theoretical) internal rate of return (IRR, overall interest rate) earned by an investor who buys the bond today at the market price, assuming that the bond is held until maturity, and that all coupon and principal payments are made on scheduleYield to Maturity (Estimated) (%) The estimated yield to maturity using the shortcut equation explained below, so you can compare how the quick estimate would compare with the converged solution Current Yield (%) Simple yield based upon current trading price and face value of the bondYIELD(settlement, maturity, rate, pr, redemption, frequency, basis) Important Dates should be entered by using the DATE function, or as results of other formulas or functions For example, use DATE(08,5,23) for the 23rd day of May, 08



Bonds Yield To Worst Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-01-c4613a2a2029466a960d9e3594841a03.jpg)


Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity
The yield to maturity (YTM) of a bond is the internal rate of return (IRR) if the bond is held until the maturity date In other words, YTM can be defined as the discount rate at which the present value of all coupon payments and face value is equal to the current market price of a bondYield to Maturity (YTM) – otherwise referred to as redemption or book yield Yield Yield is defined as an incomeonly return on investment (it excludes capital gains) calculated by taking dividends, coupons, or net income and dividing them by the value of the investmentYield to maturity (YTM) is the annual effective return that would be earned on a bond if it is held till its maturity Expressed as an annual percentage, the yield tells investors how much income they will earn each year relative to the cost of their investment Formula to calculate yield to maturity



Bond Valuation Wikipedia
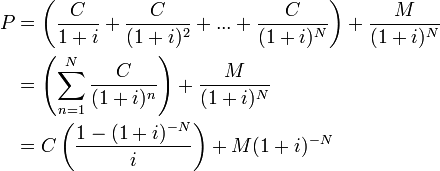


Valuing Bonds Boundless Finance
Step by Step Calculation of Yield to Maturity (YTM) Step 1 Gathered the information on the bondlike its face value, months remaining to mature, the current market price Step 2 Now calculate the annual income available on the bond, which is mostly the coupon, and it could be paid Step 3Plugging in the calculation formula, you calculate the yield as follows 1 (07/2) 2 – 1 = 7123% To see how the number of annual coupon payments received affects the effective yield on your bond, let us do another effective yield calculation that assumes you receive monthly coupon payments – 12 interest payments each yearThus, yield to call (YTC) can be defined as the internal rate of return (IRR) if a bond is expected to be redeemed before the maturity date Yield to call can also be defined as the discount rate at which the present value of all coupon payments (left to call date) and the call value are equal to the bond's current market price Formula
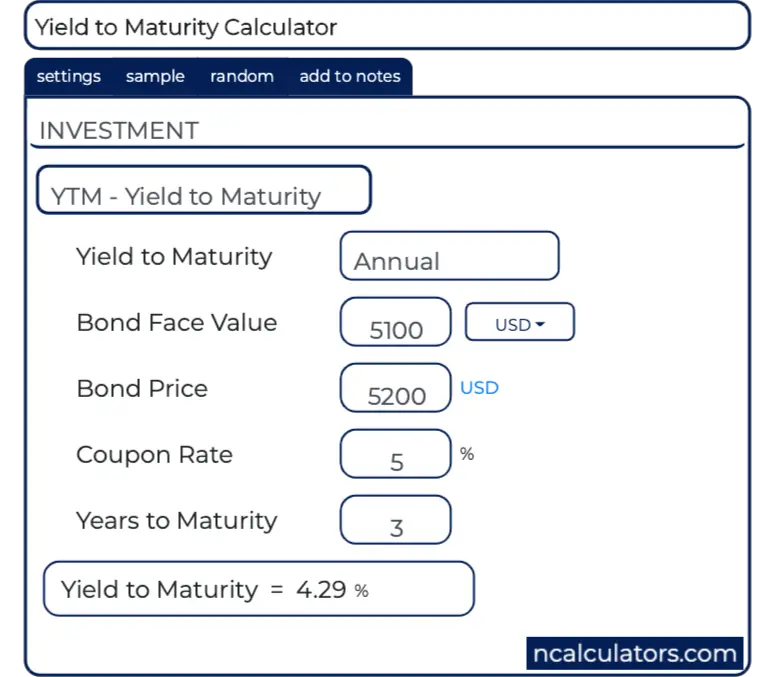


Yield To Maturity Ytm Calculator



Calculating The Yield To Maturity Ytm Of A Bond Financial Management
Use the formula = ∗ ((− (/ ())) /) / (()), where, P = the bond price, C = the coupon payment, i = the yield to maturity rate, M = the face value and n = the total number of coupon payments If you plug the 1125 percent YTM into the formula to solve for P, the price, you get a price of $A bond's yield to maturity, or YTM, reflects all of the interest payments from the time of purchase until maturity, including interest earned on interest The formula for calculating YTM is as follows Let's work it out with an example Par value (face value) = Rs 1,000 / Current market price = Rs 9 / Coupon rate = 10%, which means anThe formula for Bond Yield can be calculated by using the following steps Step 1 Firstly, determine the bond's par value be received at maturity and then determine coupon payments to be received periodically



How To Calculate Yield For A Callable Bond The Motley Fool



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity Definition Equation Example Financial Accounting Class Video Study Com
Even though the yieldtomaturity for the remaining life of the bond is just 7%, and the yieldtomaturity bargained for when the bond was purchased was only 10%, the annualized return earned over the first 10 years is 1625% This can be found by evaluating (1i) from the equation (1i) 10 = (2584/573), givingYield to maturity (YTM) is the annual return that a bond is expected to generate if it is held till its maturity given its coupon rate, payment frequency and current market price Yield to maturity is essentially the internal rate of return of a bond ie the discount rate at which the present value of a bond's coupon payments and maturity value is equal to its current market priceLet's take an example to understand how to use the formula Let us find the yieldtomaturity of a 5 year 6% coupon bond that is currently priced at $850 The calculation of YTM is shown below



Yield To Maturity Ytm And Yield To Call Ytc alectures Com



Ytm Formula Excel
The yield to maturity is found in the present value of a bond formula For calculating yield to maturity, the price of the bond, or present value of the bond, is already known Calculating YTM is working backwards from the present value of a bond formula and trying to determine what r is Example of Yield to Maturity FormulaThe equation for Yield to Maturity (YTM) is as follows, where c is the annual coupon payment, Y is the number of years to maturity, r is the YTM, B is the par value of the bond and P is the price of the bondYield to Maturity Sarah received a $100 bond as a graduation gift The longterm bond was set to mature 15 years from the date it was issued There's still five more years remaining until it matures



Thorough Description Of Yield To Maturity Personal Finance Money Stack Exchange



How Do I Calculate Yield To Maturity Ytm With A Simple Handheld Calculator For Semiannual Payments Personal Finance Money Stack Exchange
The yield to maturity (YTM), book yield or redemption yield of a bond or other fixedinterest security, such as gilts, is the (theoretical) internal rate of return (IRR, overall interest rate) earned by an investor who buys the bond today at the market price, assuming that the bond is held until maturity, and that all coupon and principal payments are made on scheduleHow to Calculate Yield to Maturity For example, you buy a bond with a $1,000 face value and an 8% coupon for $900 The bond pays interest twice a year and matures in 5 years Enter "1,000" as the face value, "8" as the annual coupon rate, "5" as the years to maturity, "2" as the coupon payments per year, and "900" as the current bond priceFormula Under the yield to maturity approach, cost of debt is calculated by solving the following equation for r There is no algebraic solution to the above equation, but we can employ the hitandtrial method We can also use Excel YIELD function Please see the article on YIELD TO MATURITY to study alternative methods for solving for r



Calculate The Ytm Of A Coupon Bond Youtube



Bond Discounting I Types I Examples I Formula I Bonds Valuation
For callable bonds, knowing the coupon rate and yield to maturity only tells you part of the story To make informed investment decisions, you need to know what the bond's yield would be if it(iii) Determination of yield and maturity The right to issue the PIK instrument is treated as an option to defer the initial interest payment until maturity Yield determined without regard to the option is 1055 percent, compounded annually Yield determined by assuming U exercises the option is 1032 percent, compounded annuallyCalculating yield to maturity involves working backwards from the current price of the bond to see what its approximate yield is in the current market Investors can use the yieldtomaturity


Q Tbn And9gctmjjcknhq5z6xqz1cb0 Ujolevox3tjfw K1tbrzk W Ikim Usqp Cau
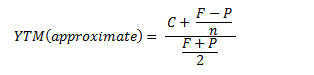


What Is The Difference Between Irr And The Yield To Maturity The Motley Fool
Y T M = Face Value Current Price n − 1 where n = number of years to maturity Face value = bond's maturity value or par value Current price = the bond's price today \begin{aligned} &YTMThe current yield is 0619 or 619%, here's how to calculate ($5750 coupon / $922 current price) The yield to maturity is the yield earned on a bond based on the cash flows promised from the date of purchase until the date of maturity;Yield to Maturity Formula Example #2 Consider a market bond issued in the market having a bond period of 5 years and an interest coupon rate of 9% Consider the issue price of Bond at $ 90, and redemption value be $ 105 Calculate the posttax Yield to Maturity for the investor where the rate of normal Income tax can be assumed at 30% and
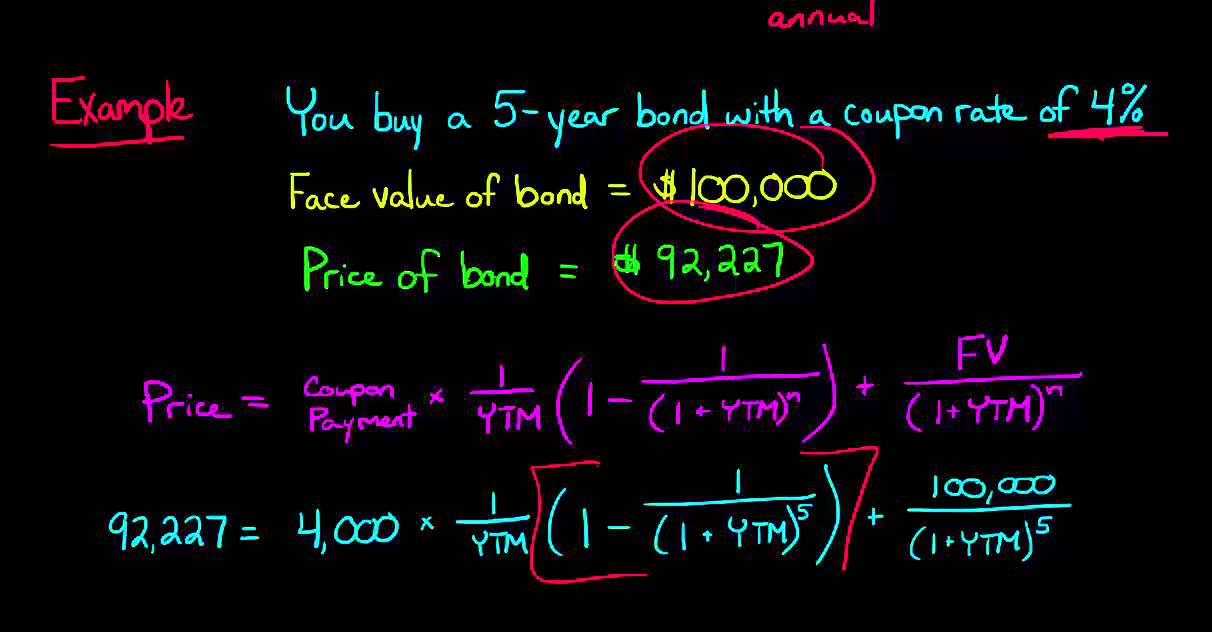


Calculating The Yield Of A Coupon Bond Using Excel Youtube



What Is A Zero Coupon Bond
However, YTM is not current yield – yield to maturity is the discount rate which would set all bond cash flows to the current price of the bond You can find more information (including an estimated formula to calculate YTM) on the yield to maturity calculator pageThe calculator uses the following formula to calculate the yield to maturity P = C×(1 r)1 C×(1 r)2 C×(1 r)Y B×(1 r)Y Where P is the price of a bond, C is the periodic coupon payment, r is the yield to maturity (YTM) of a bond, B is the par value or face value of a bond, Y is the number of years to maturityTo apply the yield to maturity formula, we need to define the face value, bond price and years to maturity For example, if you purchased a $1,000 for $900 The interest is 8 percent, and it will mature in 12 years, we will plugin the variables



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity Definition Equation Example Financial Accounting Class Video Study Com



Perpetuity Yield To Maturity Youtube
The calculator uses the following formula to calculate the yield to maturity P = C×(1 r)1 C×(1 r)2 C×(1 r)Y B×(1 r)Y Where P is the price of a bond, C is the periodic coupon payment, r is the yield to maturity (YTM) of a bond, B is the par value or face value of a bond, Y is the number of years to maturityYield to Maturity Formula Example #2 Consider a market bond issued in the market having a bond period of 5 years and an interest coupon rate of 9% Consider the issue price of Bond at $ 90, and redemption value be $ 105 Calculate the posttax Yield to Maturity for the investor where the rate of normal Income tax can be assumed at 30% andThe Yield to Maturity Unlike the current yield, the yield to maturity (YTM) measures both current income and expected capital gains or losses The YTM is the internal rate of return of the bond, so it measures the expected compound average annual rate of return if the bond is purchased at the current market price and is held to maturity



How To Calculate Yield For A Callable Bond The Motley Fool
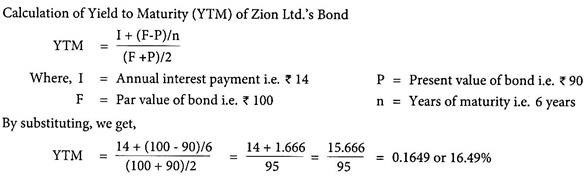


Yield To Maturity Ytm Of Debt Security Firm Financial Management
Whereas, the current yield is the annual coupon income divided by the current price of the bond


Ytm Yield To Maturity Calculator


Learning Unit 09 Interest Rate



Bonds Part Iii Pricing Financial Modeling History



Yield To Maturity Formula Ppt Download



Bond Yield Calculator



Coupon Rate Vs Yield Rate For Bonds Wall Street Oasis



Calculating The Yield To Maturity With Default Risk Youtube


Stata Codes For Calculating Yield To Maturity For Coupon Bonds Stataprofessor


Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula And Example


Yield To Maturity Definition How To Calculate Ytm Pros Cons



Quant Bonds Yield


Yield Curve How Yield Curve Changes Affect Annuities


Cost Of Debt Definition Formula Calculation Example


Understanding Interest Rates Ppt Download
/dotdash_Final_Yield_to_Worst_YTW_Oct_2020-01-cabc0d0cf5b64ef0b4f72afb4888b3aa.jpg)


Yield To Worst Ytw Definition



Fixed Income Analysis Week 2 Measuring Yields And Returns Ppt Download


Learn To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Ms Excel
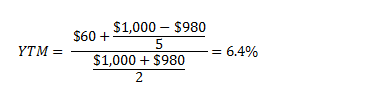


What Is The Difference Between Irr And The Yield To Maturity The Motley Fool



How To Calculate Yield For A Callable Bond The Motley Fool
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-02-10d2adc981ea475eb2165a5ec13082ed.jpg)


Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity Definition Equation Example Financial Accounting Class Video Study Com


Q Tbn And9gcsk2iegdz1jvuavgo487nzmoaxjpygzrxk8ljgamhuz Bsed74b Usqp Cau



Yield To Maturity For Bond Valuation For Ca Final Sfm Video Classes Online Satellite Offline Youtube
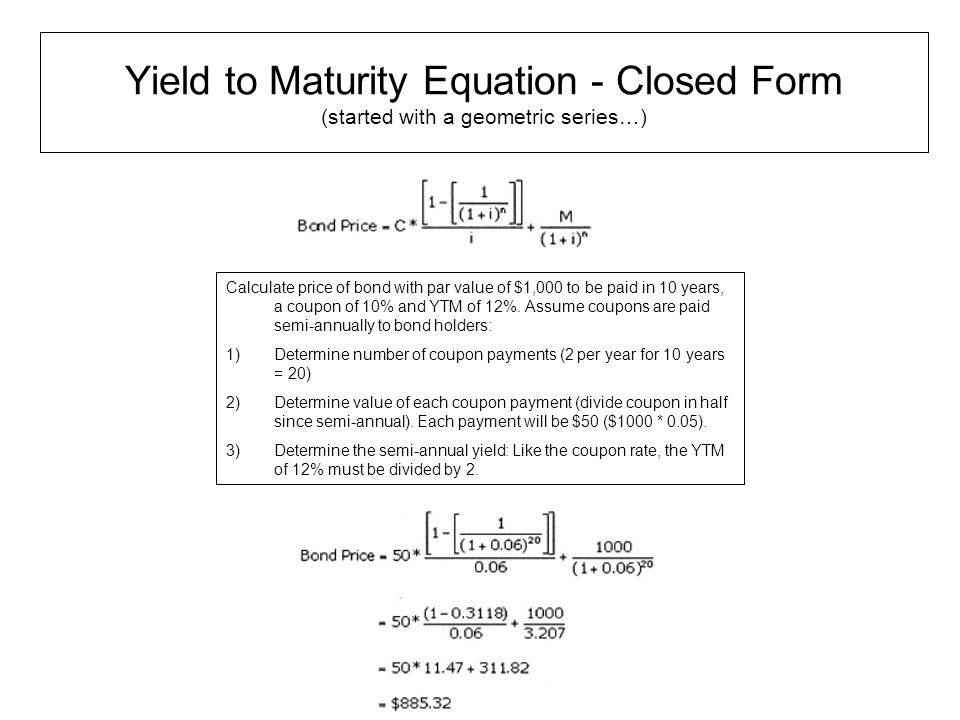


Yield To Maturity Formula Ppt Video Online Download



Vba To Calculate Yield To Maturity Of A Bond
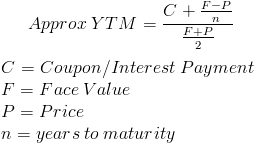


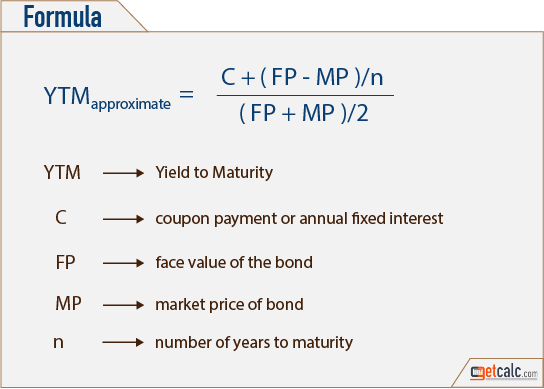
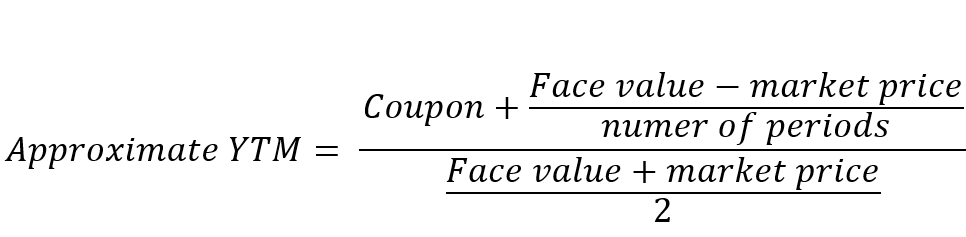
Yield To Maturity Approximate Formula With Calculator



Calculating The Yield To Maturity Mastering Python For Finance Second Edition
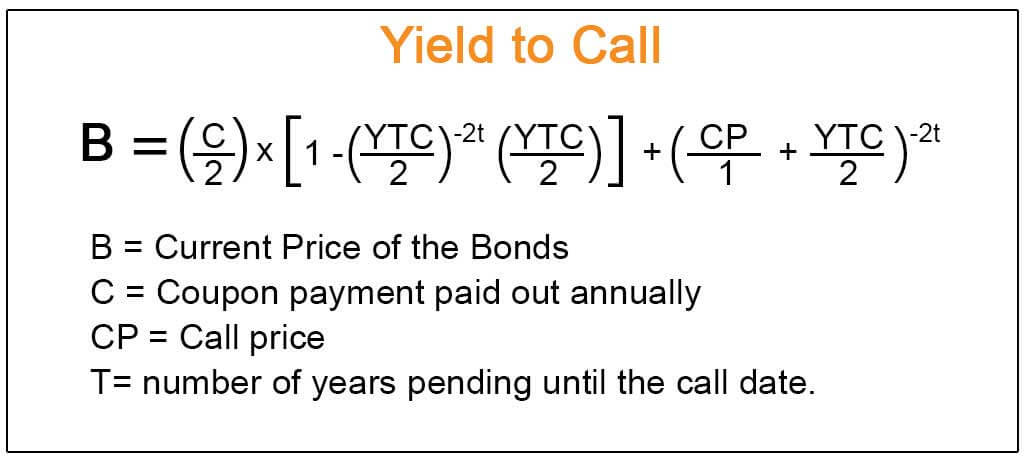


Yield To Call Definition Formula How To Calculate Yield To Call Ytc
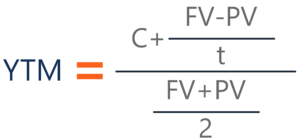


Yield To Maturity Ytm Overview Formula And Importance
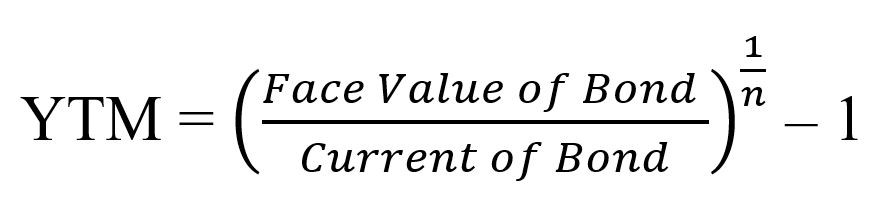


What You Must Know On Bond Valuation And Yield To Maturity Acca Afm Got It Pass


Yield To Maturity Components And Examples Of Yield To Maturity



What Is Yield To Maturity How To Calculate It Scripbox
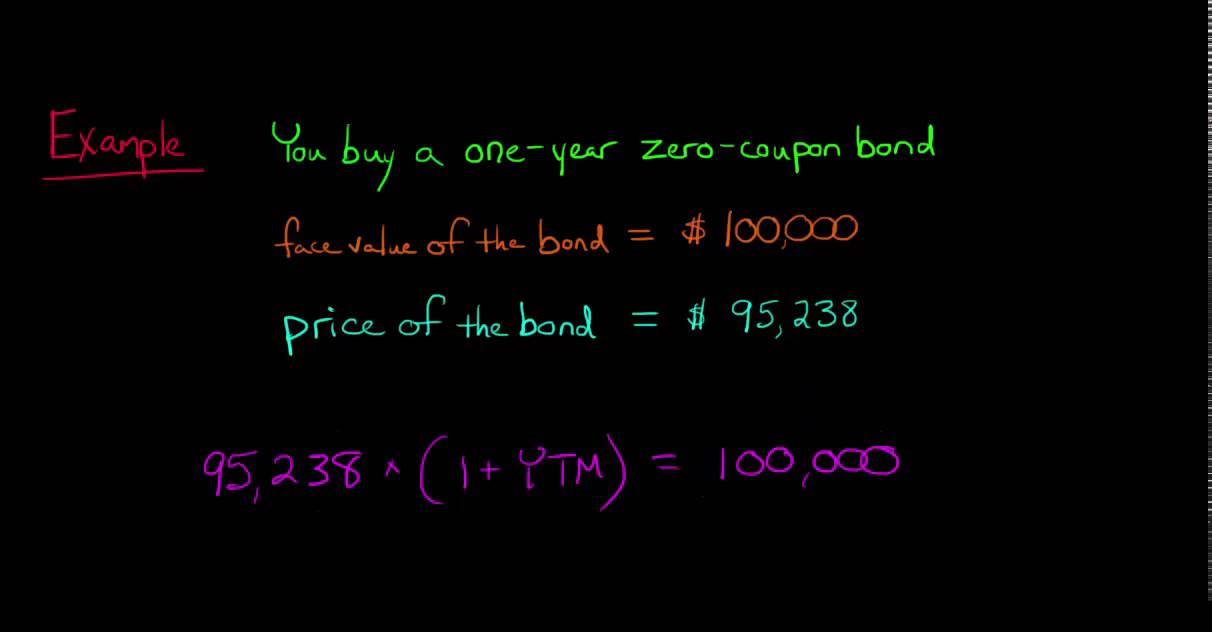


Calculating The Yield Of A Zero Coupon Bond Youtube
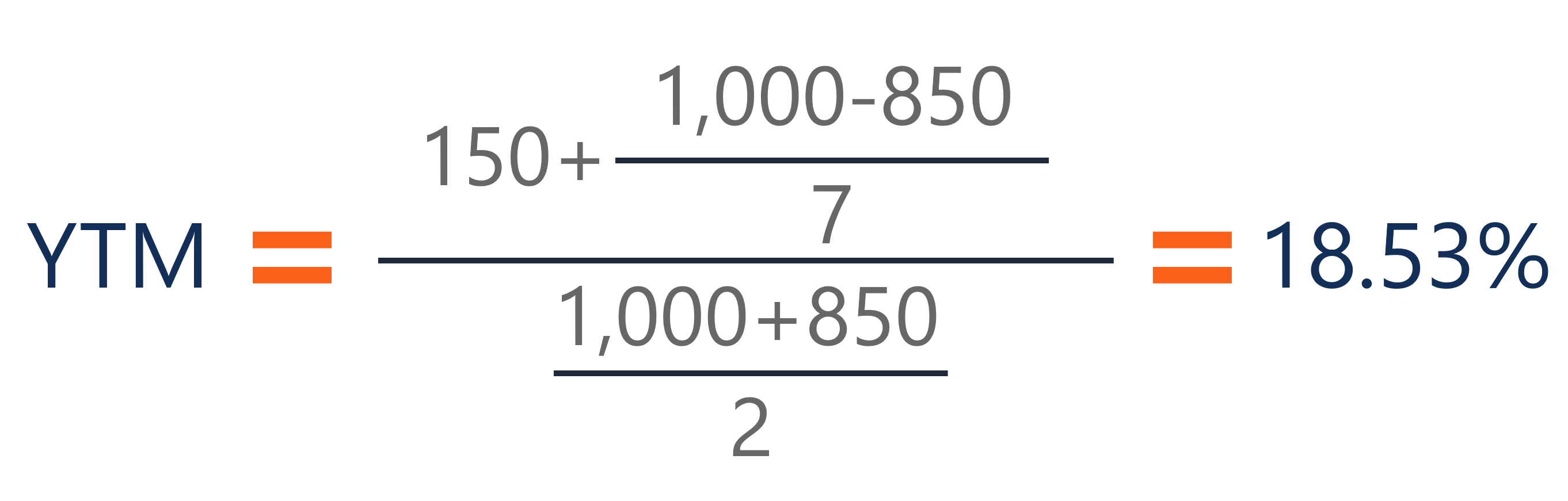


Yield To Maturity Ytm Overview Formula And Importance
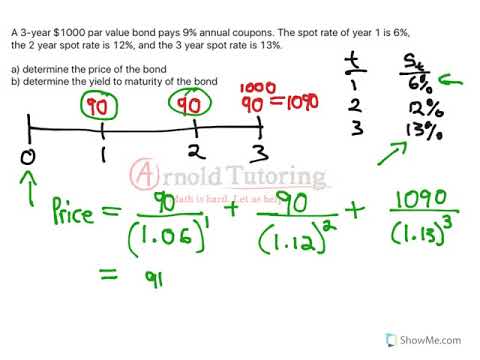


Bonds Spot Rates Vs Yield To Maturity Youtube



Yield To Maturity Fixed Income
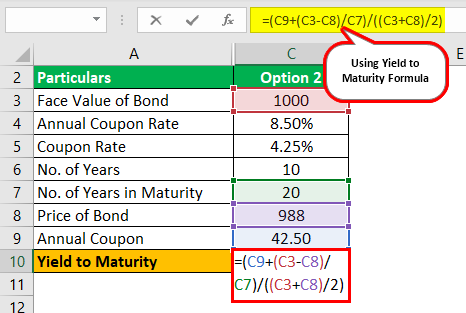


Yield To Maturity Formula Step By Step Calculation With Examples
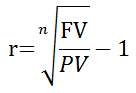


Bond Yields Nominal And Current Yield Yield To Maturity Ytm With Formulas And Examples
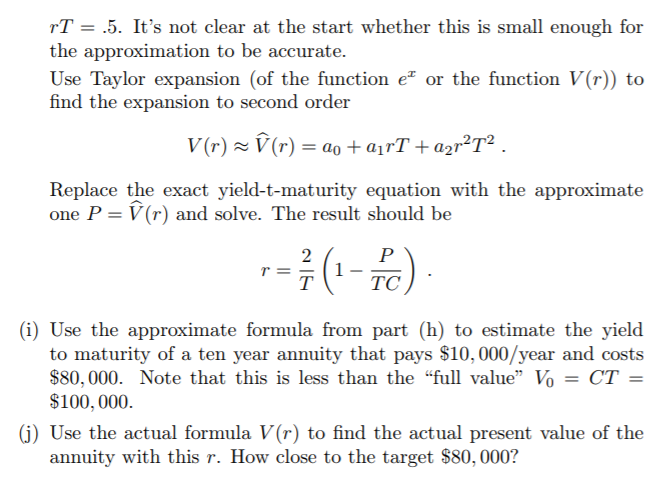


F Yield To Maturity Consider A Financial Inst Chegg Com


2


Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula Method Example Approximation Excel



Solving For A Bond S Yield To Maturity With Semiannual Interest Payments Youtube



Yield To Maturity
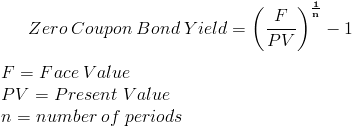


Zero Coupon Bond Yield Formula With Calculator
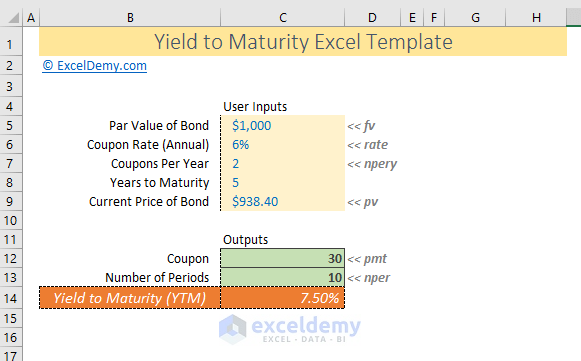


How To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Excel With Template Exceldemy
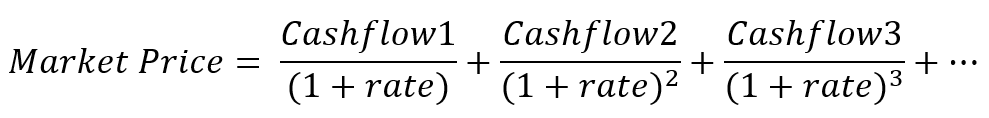


Stata Codes For Calculating Yield To Maturity For Coupon Bonds Stataprofessor
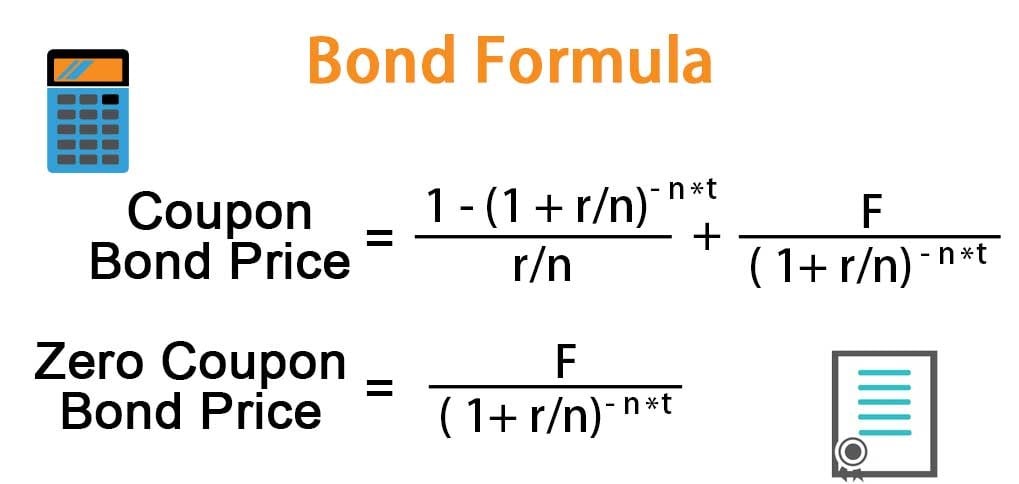


Bond Formula How To Calculate A Bond Examples With Excel Template
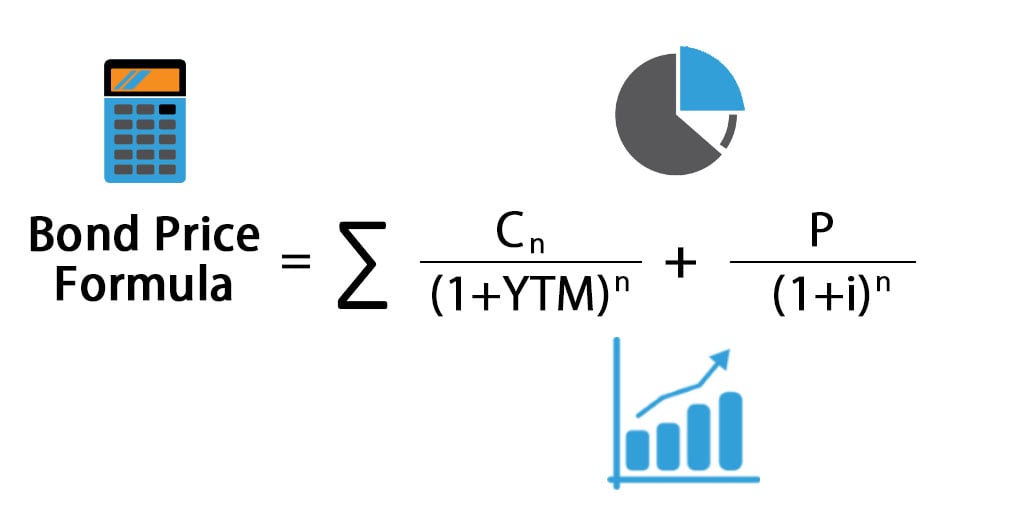


Bond Pricing Formula How To Calculate Bond Price
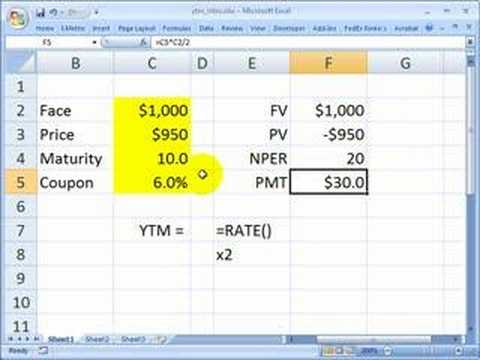


Frm How To Get Yield To Maturity Ytm With Excel Ti Ba Ii Youtube



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity Definition Equation Example Financial Accounting Class Video Study Com



Bond Valuation
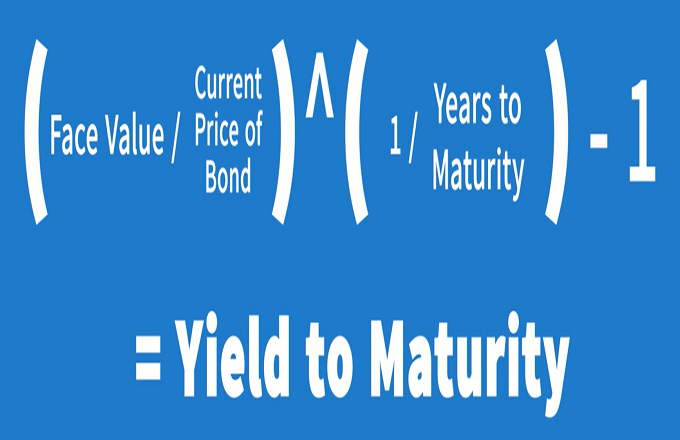


Calculating Yield To Maturity Of A Zero Coupon Bond



Methods To Calculate Yield To Maturity Ytm Docx There Are Various Methods To Calculate Ytm Yield To Maturity And Present Value Of A Bond The Yield To Course Hero



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity Definition Equation Example Financial Accounting Class Video Study Com



Bond Yield Calculator



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity Definition Equation Example Financial Accounting Class Video Study Com



Bonds Yield To Maturity Example 1 Youtube
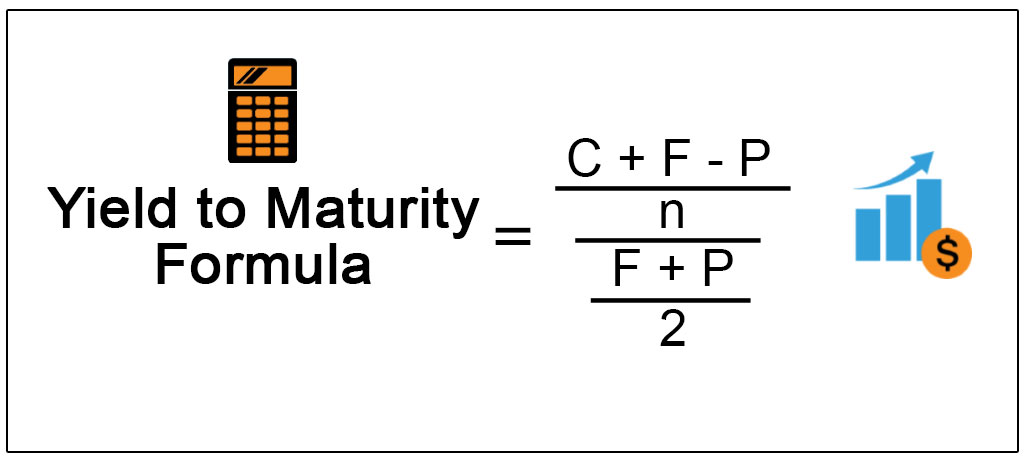


Yield To Maturity Formula Step By Step Calculation With Examples
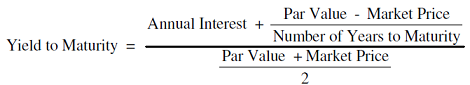


What Is Yield And How Does It Differ From Coupon Rate



Contents Method 1 Pricing Bond From Its Yield To Maturity Calculating Yield From Bond Price Method 2 Pricing Bond From Duration Pricing Bond From Ppt Download



Bond Yield Calculator


Q Tbn And9gcr1nwve1x90e Wi Dy2c5vtgbuvi3hylgxygwbapj2gpg7prety Usqp Cau
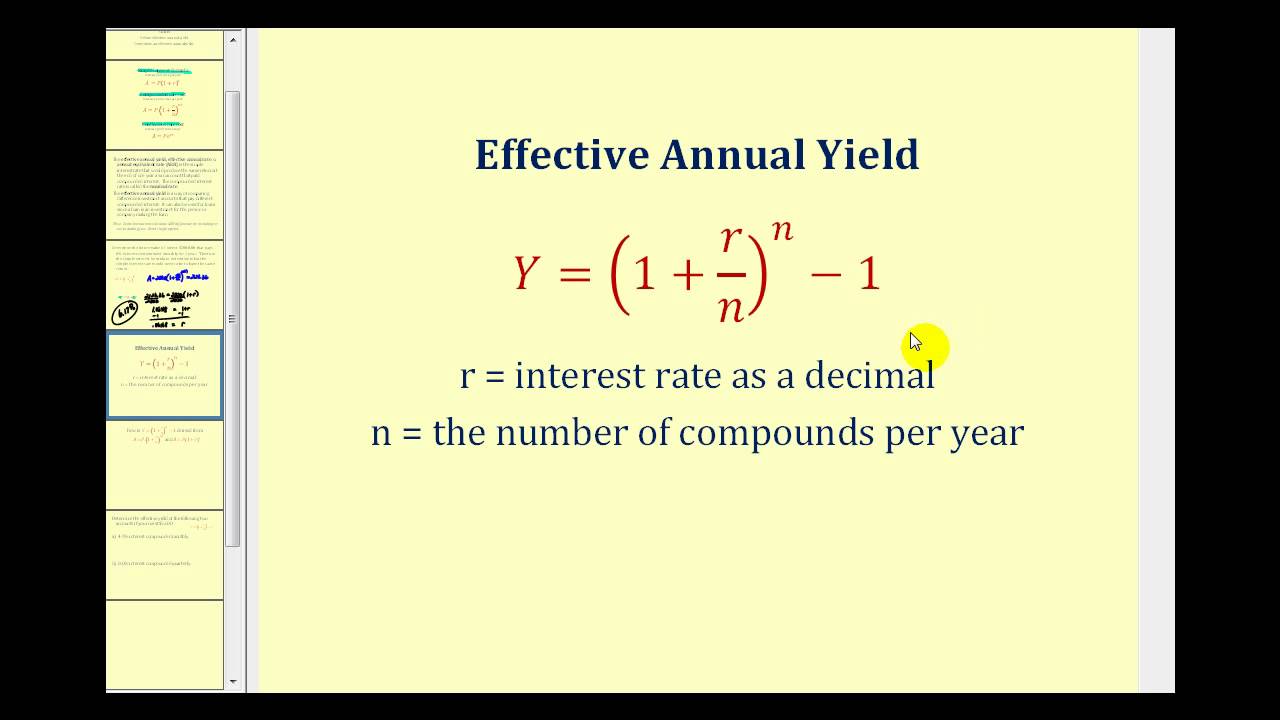


Determining The Effective Yield Of An Investment Youtube


1
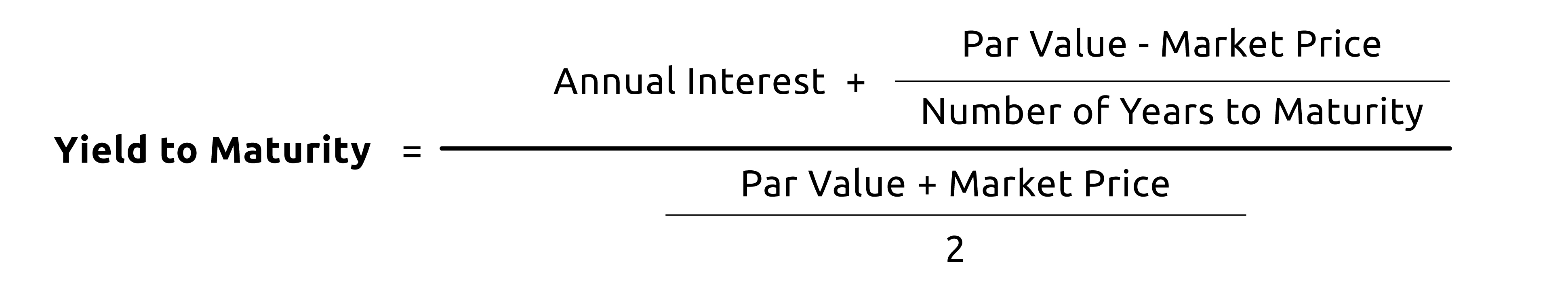


Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula Calculations In Debt Mutual Fund Nippon India Mutual Fund
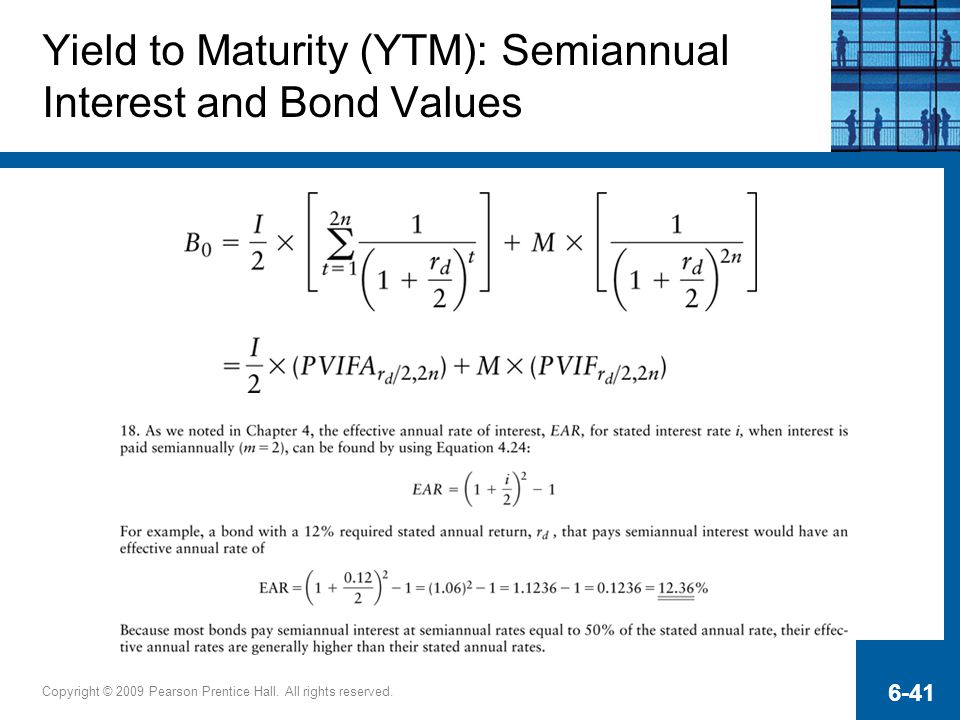


Interest Rates And Bond Valuation Ppt Video Online Download
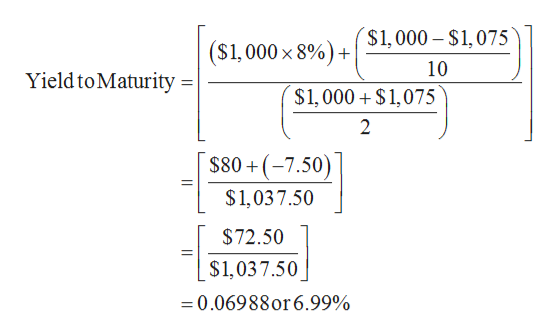


Answered How Do You Calculate Yield To Maturity Bartleby
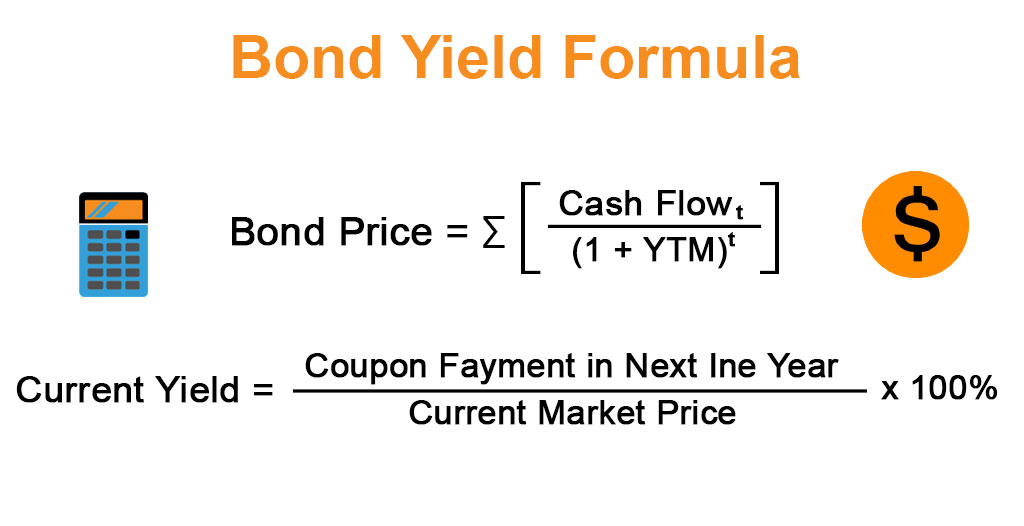


Bond Yield Formula Calculator Example With Excel Template



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity 9 Steps With Pictures



Berk Chapter 8 Valuing Bonds



How To Calculate Bond Value 6 Steps With Pictures Wikihow



What Is Yield To Maturity How To Calculate It Scripbox



Solved 3 Bonds And Their Valuation Calculating Yields C Chegg Com



Yields To Maturity On Zero Coupon Ronds Bond Math
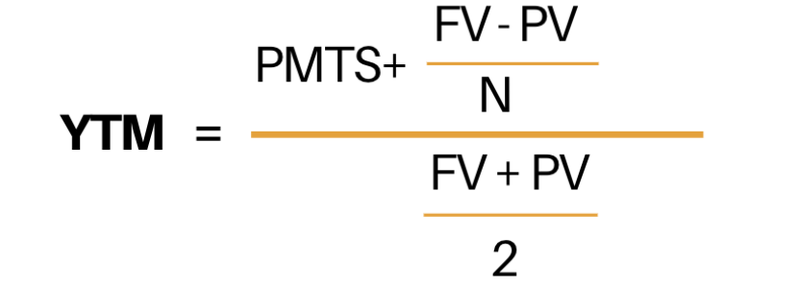


What Is Yield To Maturity Ytm Millionacres



Vba To Calculate Yield To Maturity Of A Bond


コメント
コメントを投稿